Tokyo Metropolitan University
Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering
Transfer Laboratory
Research Projects
Simultaneous Imaging of Temperature and Concentration in Microfluidic Channel
For microfluidic applications, it is necessary to measure and control temperature
and concentration distributions when chemical reaction and diffusion occur
between two liquid solutions. We have developed a near-infrared (NIR) imaging
method for measuring the temperature and concentrations of aqueous solutions
simultaneously. This method is based on the spectral characteristics of
an NIR absorption band of water. The images can also be used for the determination
of diffusion coefficients of solutes in water and their temperature dependence.
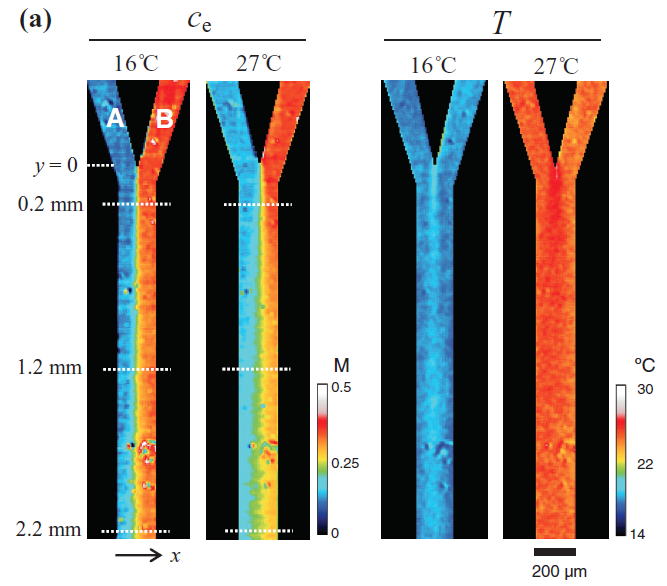
Simultaneous images of the ethanol concentration, ce, and the temperature, T in a Y-shaped microfluidic channel with the depth of 0.045 mm. Water and
ethanol-water mixture with ce = 0.43 M (2.0 wt %) flowed in the main channel through Branch A and Branch
B, respectively.The set temperatures of the whole microfluidic chip are
16°C and 27°C. Kakuta et al., Meas. Sci. Technol. 27 (2016) 115401.
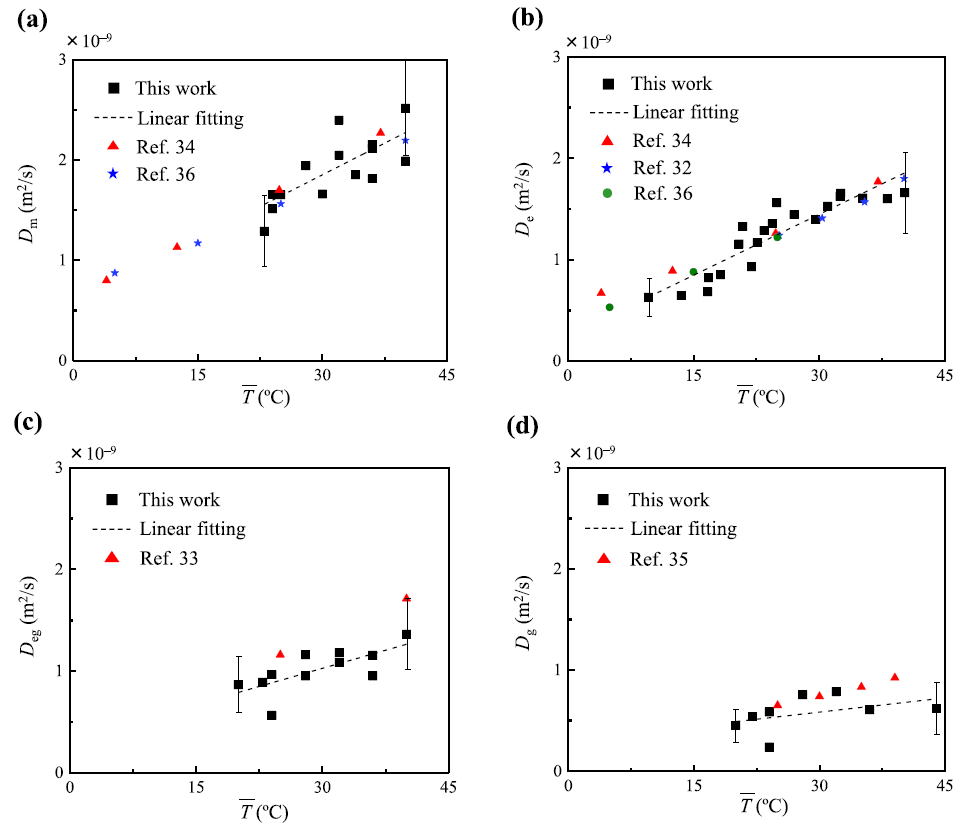
Plots of the diffusion coefficients (D) of (a) methanol, (b) ethanol, (c) ethylene glycol, and (d) glucose in
water as functions of the temperature measured by the NIR imaging method.
Error bars are indicated for the plots only at the minimum and maximum.
The literature values are plotted for comparison. Yamashita et al., Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 4 (2018) 035030.
Near-infrared Chemical Imaging
We have developed a near-infrared imaging method to simultanesouly measure
the concentrations of reactants and products during chemical reactions.
In particular, this method is useful for aqueous acid-base reactions.
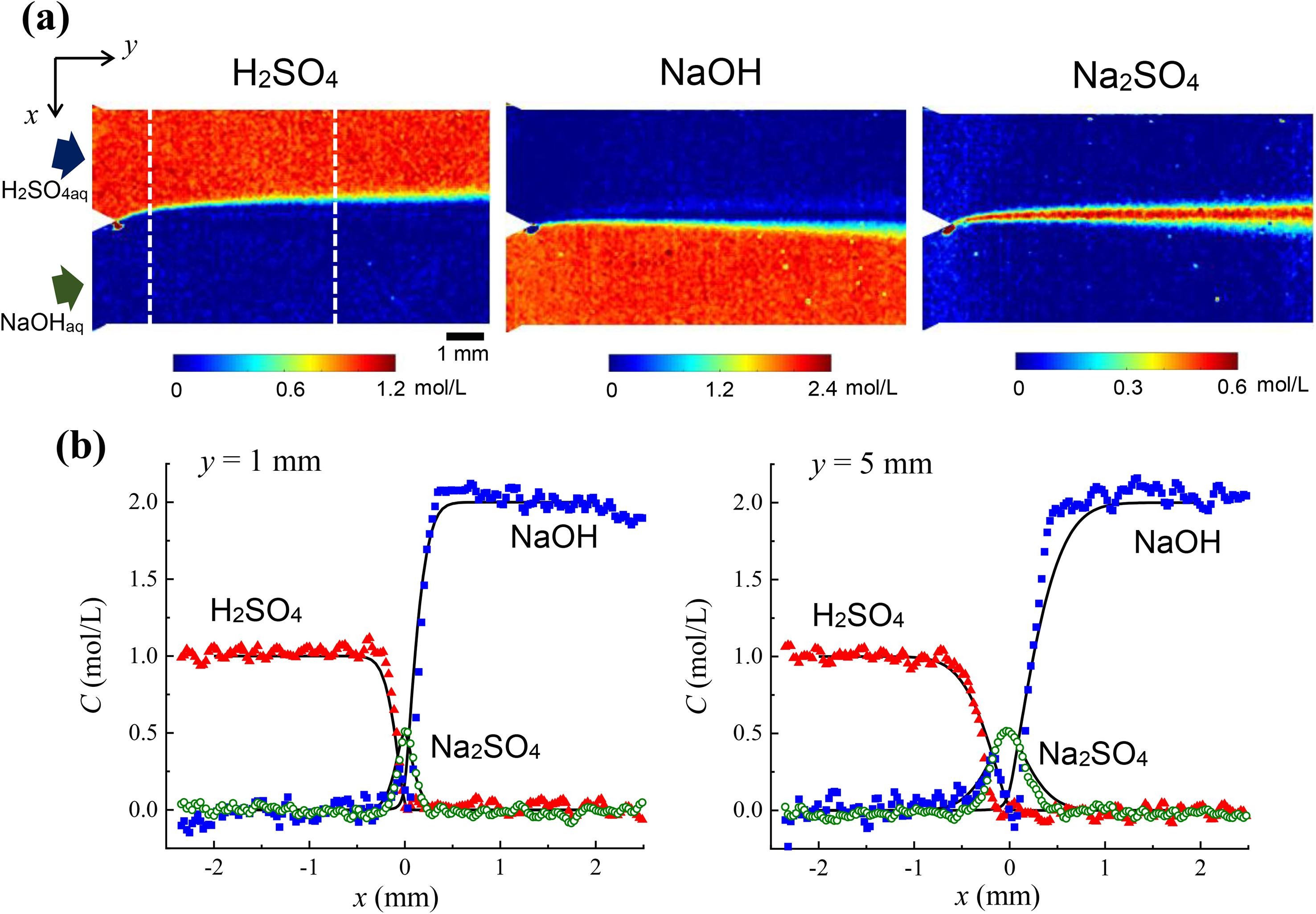
(a) Concentration images of H2SO4, NaOH, and Na2SO4 at steady-state for a mean flow velocity of 0.15 mm/s when 1.0 mol/L H2SO4aq and 2.0 mol/L NaOHaq flow in the channel. (b) Line profiles at y = 1 and 5 mm (the dashed lines indicated in the left image). The solid
lines indicate simulated profiles. Uema et al, Chem. Eng. J. 403 (2021) 126338.
Liquid-Liquid Interface Instability
The interface between two different liquids tends to become unstable mainly
due to the density difference. In particular, when a chemical reaction
occurs at the interface, the concentration and density profiles become
complicated, leading to the instability. We observe and investigate the
instability quantitatively using the NIR imaging method that shows the
concentration profiles of multiple substances.
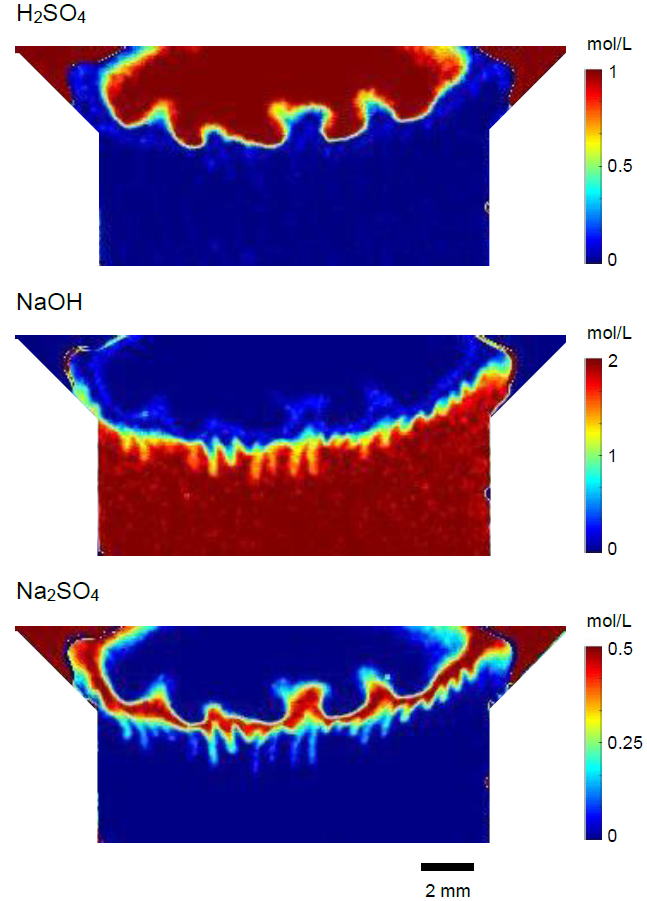
Concentration maps of the three components at 60 s after the H2SO4 aqueous solution contacted the NaOH one in a glass cell. The NIR imaging method was used for this simultaneous measurement. With the neutralization reaction at the interface between the two solutions, the interface instability occurs, indicating that the concentration patterns are different between the top and bottom sides of the interface.
Temperature Distribution in Water with a Small Heat Source
A method for predicting temperatures distributions in liquid is being developed,
based on a near-infrared absorption imaging and an inverse problem solution.
Particularly in the case of an asymmetric temperature distribution, it
can be predicted by the inverse Abel transform of the measured absorbance
profile. This method will enable to visualize transient temperature distributions
near point-like heat sources.
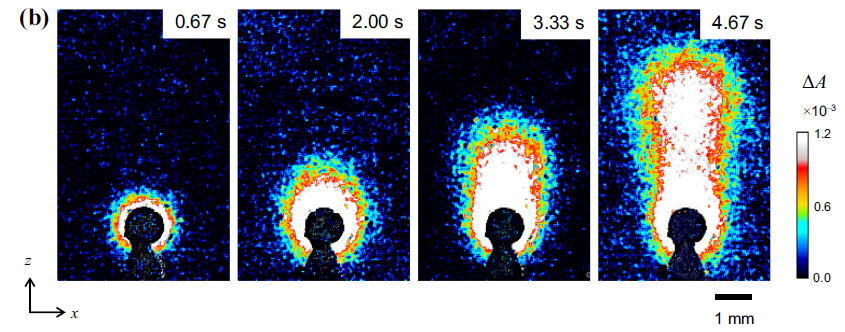
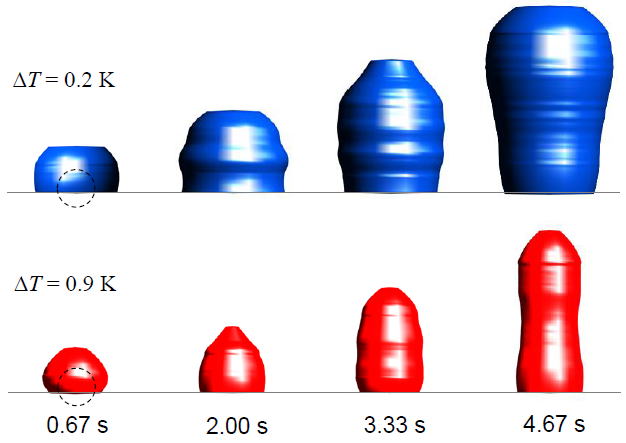
(Left) Near-infrared absorbance images of a 10-mm-thick water layer containing a 1-mm-diameter steel sphere heated by electromagnetic induction. As the absorbance at a certain wavelength depends on the water temperature, the images clearly demonstrate the temperature increase and free convection. (Right) Three-dimensional isotherm surfaces of 0.2 K and 0.9 K, constructed from the absorbance images. Kakuta et al., Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 137 (2019) 847.
Thermal Applications of Micro/Nano-Magnetic Particles
Magnetic particles have a potential to be used for chemical engineering
and biomedical applications such as hyperthermia. In this study, magnetic
particles are aggregated locally in a microfluidic channel and the surrounding
temperature distributions are measured usina a near-infrared imaging technique.
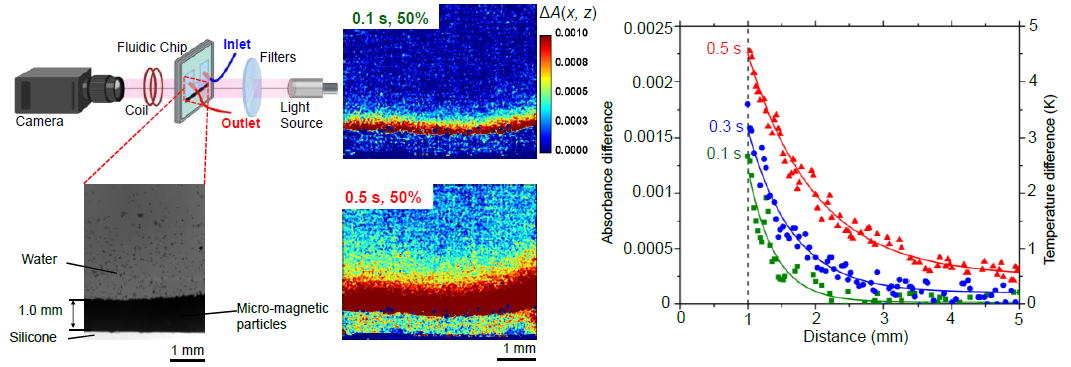
Temperature distributions of water near a micro-magnetic particle layer
were measured. Han and Kakuta, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 115 (2020) 110087.
Glow-Corona-Assisted Spectrochemical Analysis
Glow corona is stable microplasma generated at the tip of a needle electrode
under atmospheric pressure. The glow corona is so small that it can react
with minute surface areas of liquid and solid materials. During the reaction,
the absorption spectra are continuously measured to analyze molecular structure
changes.
Near-Infrared Glucose Measurement
For non-invasive measurement of glucose in blood of the human body, we have developed a novel optical device with signal analysis techniques.